
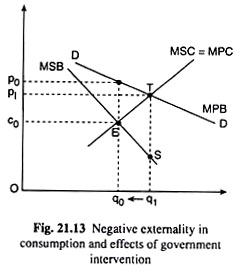
This means the (marginal) private benefit for junk food consumption (i.e. Eating junk food regularly affects your health which represents a third party cost to the health services provided by the government. Oh and don’t eat big macs or junk food too.
#Positive externality of consumption download#
Want a closer look? Download these Positive and Negative Externality notes. Positive and Negative Externality Notes with Diagrams

As a result, the government may have to intervene in the market to reduce the third party cost e.g. Externalities are a type of market failure as it disrupts the usual operation of the market mechanism, which maximises consumer/producer surplus but does not take into account third parties. Methane contributes to global warming and climate change disasters, incurring a cost to third parties. Similarly, large amounts of methane is emitted when raising cattle to produce beef. Hence there is a negative production externality in tuna production. As a result, it disrupts the food chain and depletes a source of protein for coastal communities (cost to third party). The large amount of tuna overfishing to produce canned tuna or sushi, causes the species to be endangered. When you eat a beef steak or some tuna, you are the supporting the negative externality involved in producing these foods. Positive and Negative Externality Examples & Explanation: – A third party is any individual or group other than the producer or consumer of the good. – Positive externalities arise when the production or consumption of a good creates a benefit to a third party. – Negative externalities arise when the production or consumption of a good creates a cost to a third party. Positive and Negative Externality Definitions: Relevant Exam Boards: A-Level (Edexcel, OCR, AQA, Eduqas, WJEC), IB, IAL, CIEĮdexcel Economics Notes Directory | AQA Economics Notes Directory | IB Economics Notes Directory


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
